Diseases
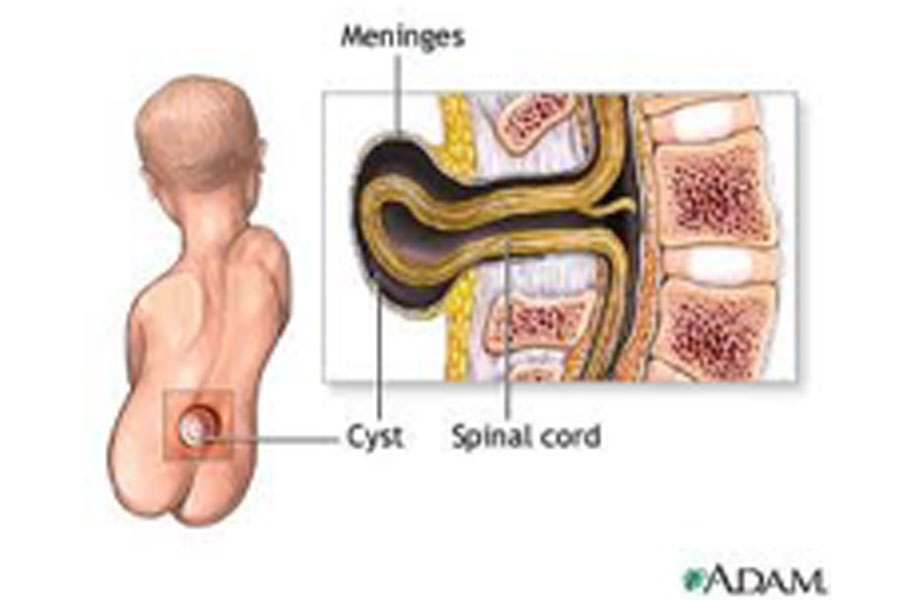
Meningocele
A protrusion of the meninges through a gap in the spine due to a congenital defect.
SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of meningocele are divided into subjective and objective. First relate mainly just to complaints of parents of child or adult patient on presence of tumor in area of prolapse of hernia. There are usually no other complaints. Size of this "tumor" may vary from lentil grains to large apple, sometimes imitating "second nose". This formation is of soft elastic consistency, sometimes its leg goes deep into root of nose. Swelling may pulsate in sync with contractions of heart, it can increase when straining (child`s screaming or crying), and decrease with pressure on it. These signs indicate on connection of tumor with cavity of skull.
Deformation of facial skeleton is additional feature of anterior meningocele and hernia of brain.
Complications and consequences
Complications with meningocele are dangerous phenomena, which usually ends with death. These include meningoencephalitis arising from ulceration of meningocele wall. However, these complications are more often result of surgical removal of hernia sac. These complications are:
1. intraoperational (shock, hemorrhage);
2. early postoperative (meningitis, meningoencephalitis, brain edema);
3. delayed postoperative (hydrocephalus, intracranial hypotension, cerebral edema, convulsions);
4. late (epilepsy, mental disorders, intellectual disabilities).
Fistula of subarachnoid space, liquorrhea, relapses of meningocele and brain hernia can be attributed to postoperative complications.
CAUSES
- There is hypothesis of meningocele development, which links occurrence of primary ectopia of meninges and brain through primary defects of skull as a result of stop of development of skull in embryonic period. Springs explains origin of meningocele and encephalocele by pathological changes of cranial vault, arising as result of meningoencephalitis, which fetus had during pregnancy. Klein believes that fetal hydrocephalus is the cause of meningocele, which leads to divergence of skull bones, and its perforation in the area of natural orifices.
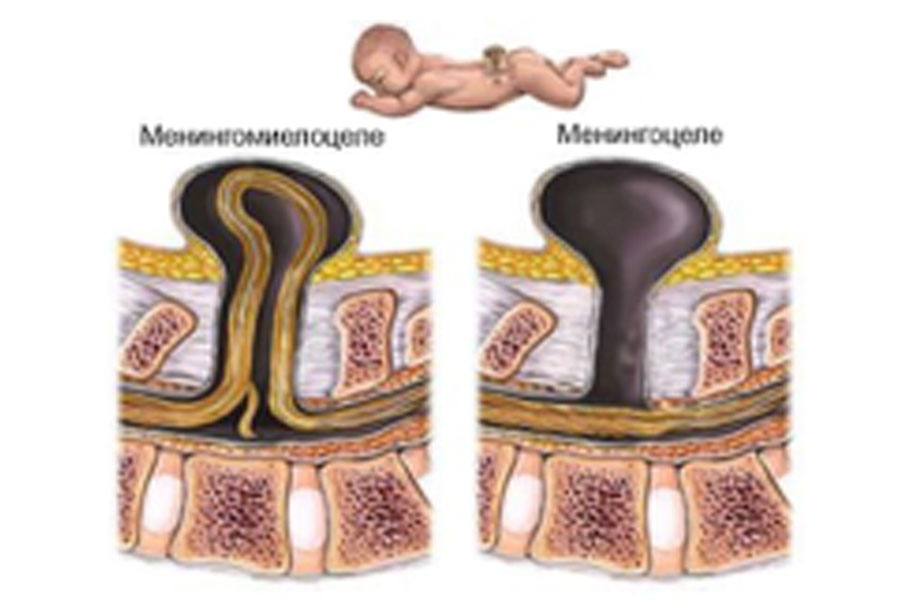
- As already mentioned, they are formed first by prolapse of meninges forming bag filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and then, if hole is sufficiently large, brain tissue also goes into this bag. Typically this prolapse occurs through hole in root of nose and glabella. Meningocele and encephalocele are divided into two types:
- midline positioned (nasofrontal);
- positioned by sides of root of nose (nasocancellous) and in inner corner of eye socket (nasoorbital).
- There are various "theories" for the origin of meningocele.


Chitradurga
Seebara, Behind Indian Oil Petrol Bunk, Basavakumara Swamy Mutt, Chitradurga - 577504
Kunigal
K Huraliborsandra, Gowdgere Post, Dhomratti Temple Road, Kunigal, Tumakuru District. - 572130
Bengaluru
36, KG Gollarapalya, Bolare (P), Kanakapura Road, Bengaluru - 560082